Key Findings
A small majority of programmes is conducted internationally (60 percent), while at the same time there is a notable level of activities carried out by Member States within their own countries (40 percent).
People at the Base of the Pyramid are especially targeted as customers and/or suppliers.
G20 Inclusive Business policies and programmes are spread across all relevant sectors, particularly agriculture, retail, manufacturing and consumer goods, and financial services.
The main topics identified in the programme reports as areas of focus are “Inclusive Business Models and Strategy,” “Gender,” “Capacity Building,” “Finance,” “Partnerships” and “Innovation.”
Marcos Athias Neto,
Director, Istanbul International Center
for Private Sector in Development, UNDP
"Inclusive businesses can become real changemakers when improving the living conditions for almost half of the world´s population who currently live below US $8 per day."
Christian Jahn, Executive Director, iBAN
Inclusive Business has gained increasing importance since the adoption of an Inclusive Business working definition by the G20 in 2011. In 2018, the Argentinian G20 presidency put Inclusive Business back on the agenda. An increasing number of projects, initiatives and policies with a focus on IB are being implemented by the Member States, invited countries and International Organizations (IOs) of the G20. As Marcos Athias Neto, Director of the Istanbul International Center for Private Sector in Development at UNDP, states, "it is immensely important for the future of Inclusive Business to have the backing of the G20 Leaders, as it was expressed under the Argentinian presidency in the G20 Leaders´ Declaration and the G20 Call on Financing for Inclusive Business. At UNDP we are delighted to be working with the G20 for many years and to co-manage a global platform. Inclusive and sustainable business models are key to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals."
In response to a call for information on IB programmes, 47 projects, initiatives and policies from these partners provided key updates on their work. Based on this information, this report highlights key findings and messages from the activities. The members reported on several factors related to their IB programmes, including: intent/objectives; geographical and target group reach; the sectors and topics of the activities; the implementation method and funding sources.
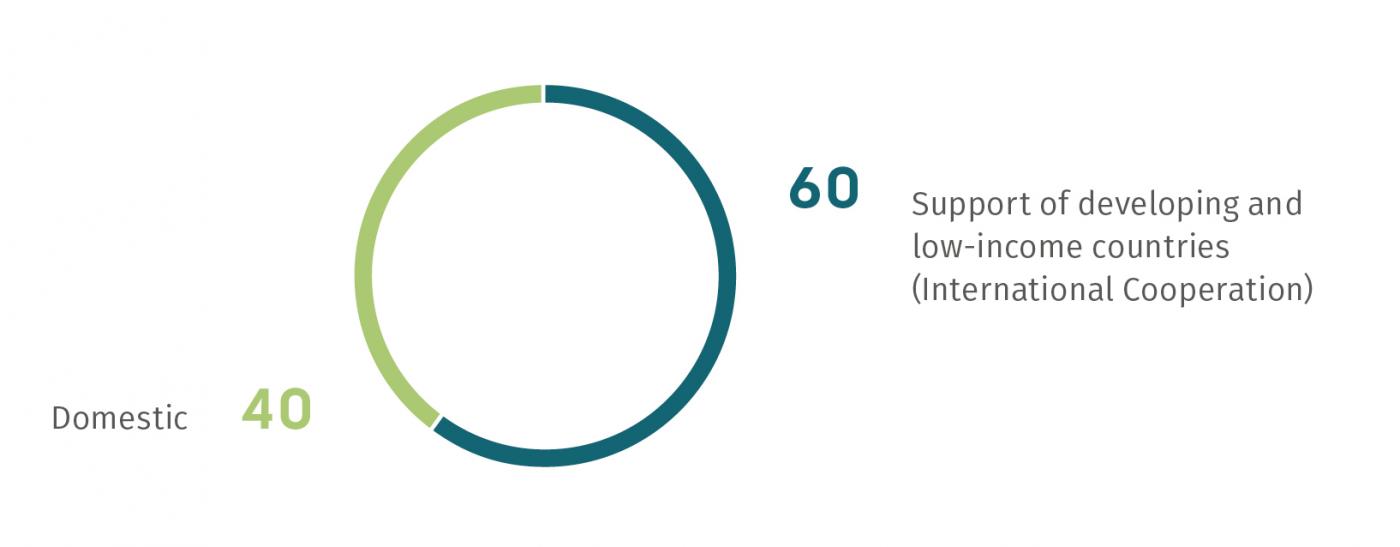
Chart: Implementation level of G20 projects
The report found that G20 Member States and International Organizations apply various different approaches. A majority of programmes are implemented by one country, while at the same time various models of multilateral partnerships and cooperation are being utilised. While some countries implement their programmes in their domestic realm, a small majority are carried out in the context of international cooperation.
People living at the Base of the Economic Pyramid (BoP) are supported by all of the programmes. However, the role they play differs. Mostly, the low-income communities are incorporated into the value chain as suppliers or customers, but some are also involved as distributors or retailers.

People at the BoP are engaged in different ways, for example as retailers or customers. Photo Credit: GIZ/Dirk Ostermeier
Additionally, it is interesting to note that some of the projects, initiatives and policies work with one specific category of BoP engagement, while others focus on various areas.
Most of the projects focus on the following sectors: Agriculture or food (29 out of 47 projects), retail, manufacturing or consumer goods (21) and financial services (18). Many programmes have stated that their projects are multi-sectoral with a varying number of sectors covered.

Agriculture is one of the main sectors that Inclusive Business policies focus on. Photo Credit: Pexels.com
In some cases, Inclusive Business is introduced as an approach to improve the living standards of the BoP within a specific sector, while in other instances it is applied as a holistic concept to encourage IB in all sectors.
While a range of topics are being addressed directly, some cross-cutting topics emerge within the reports of the 47 G20 programmes. Notably, the topic of gender plays an important role for many projects, initiatives and policies, as do financing and digital means.

Gender plays an important role for many programmes. Photo Credit: Business for Development
The G20 Framework defines four dimensions of constraints to the widespread adoption of Inclusive Business as:
- Rules and regulations
- Financial resources
- Information
- Capacity
When it comes to the type of support granted in order to address these dimensions, the reporting indicates a slightly varying application. Capacity building plays an important role and is the most applied type of support (35 percent). Financial resources and (market) information are used almost equally (27 and 26 percent respectively), whereas the fieldwork on rules and the regulatory environment is incorporated into a smaller number of programmes (12 percent).

Chart: Main types of support
Most programmes rely on either government or state-owned enterprise funding (28) or private sector funding, which accounts for the financing of 19 projects, initiatives and policies.
A large number of programmes (61 percent) receive their funds from a single type of funding source; in most cases this single type is/are government(s) and/or state-owned enterprise(s). The remaining projects obtain their financing from multiple funding sources.

Inclusive Business projects aim to continuously improve the lives of the poor. Photo Credit: GIZ/Dirk Ostermeier
This initial report provides only a snapshot of the current G20 Member States’ and other partners´ activities in the field of Inclusive Business. It needs to be continuously updated and analysed in order to inspire action. The report is designed to help practitioners use the experience on hand to initiate new projects that improve the lives of the people living at the BoP and create new jobs and growth for the whole economy. According to iBAN´s Executive Director, Dr Christian Jahn "inclusive businesses can become real changemakers when improving the living conditions for almost half of the world´s population. They are able to create triple wins: profit for business, better living conditions for the poor, and reduced government expenditure." He adds: "The world needs more of those triple wins!”
UNDP and iBAN are co-managing the G20 Global Platform on Inclusive Business (GPIB), which helps facilitate expansion efforts in Inclusive Business knowledge and capacity building world-wide. Both are prepared to continuously update the report and integrate the information and insights on the GPIB.


